Behandling af ADHD og Autismespektrumforstyrrelser
Lider du af ADHD, autisme eller asperger syndrom, så kan Institut for Hjernetræning tilbyde et effektivt og professionelt neurofeedback hjernetræningsforløb. Neurofeedback/EEG-træning er hjernetræning som bruges til behandling af ADHD og diagnoser som OCD, stress, depression, demens, PTSD, forbedring af performance, autismespektrumforstyrrelser og meget mere. Denne behandlingsmetode er hjernetræning der kan forbedre din mentale sundhed og velvære.
Ring ind og hør mere om, hvad vi kan gøre for dig
Hjernetræning er utrolig effektiv som ADHD behandling
Neurofeedback er den mest effektive metode, der findes til at træne op og styrke:
- Selektiv og vedvarende opmærksomhed
- Korttids- og arbejdshukommelse
- Kognition
- Indlæring
- Sociale færdigheder
Derudover styrker man hjernens hæmningsmekanismer og reducerer impulsivitet, hyperaktivitet, motorisk uro, indlæringsvanskeligheder og affektudbrud.
Anerkendt som den mest videnskabelige effektive behandlingsform til bl.a. ADHD
Neurofeedback-træning er så effektivt at American Academy of Pediatrics i 2012 anerkendte metoden som den videnskabelige mest effektive behandling for symptomer ved ADHD, ligestillet med medicin. Et norsk-dansk studie fra 2012 i samarbejde med Haukeland sygehus i Bergen kom også frem til samme resultat. Også flere andre studier har vist det samme.
Institut for hjernetræning tilbyder tilrettelagt QEEG-målinger.
Bestil en tid til ADHD behandling
Hvorfor vælge neurofeedback som behandlingsform til ADHD, autisme og asperger?
I modsætning til medicin som kun behandler symptomerne, kan neurofeedback:
- Stimulere en naturlig udvikling
- Styrke de neurale forbindelser i hjernen
- Skabe nye nerveforbindelser og neurale kredsløb
- Op- og nedregulere det sympatiske- og parasympatiske nervesystem.
Det vil sige at man ved neurofeedback, går ind og styrker og regulerer de defekter som ligger til grund for symptomerne.
Derfor vil de resultater man opnår med neurofeedback være permanente.
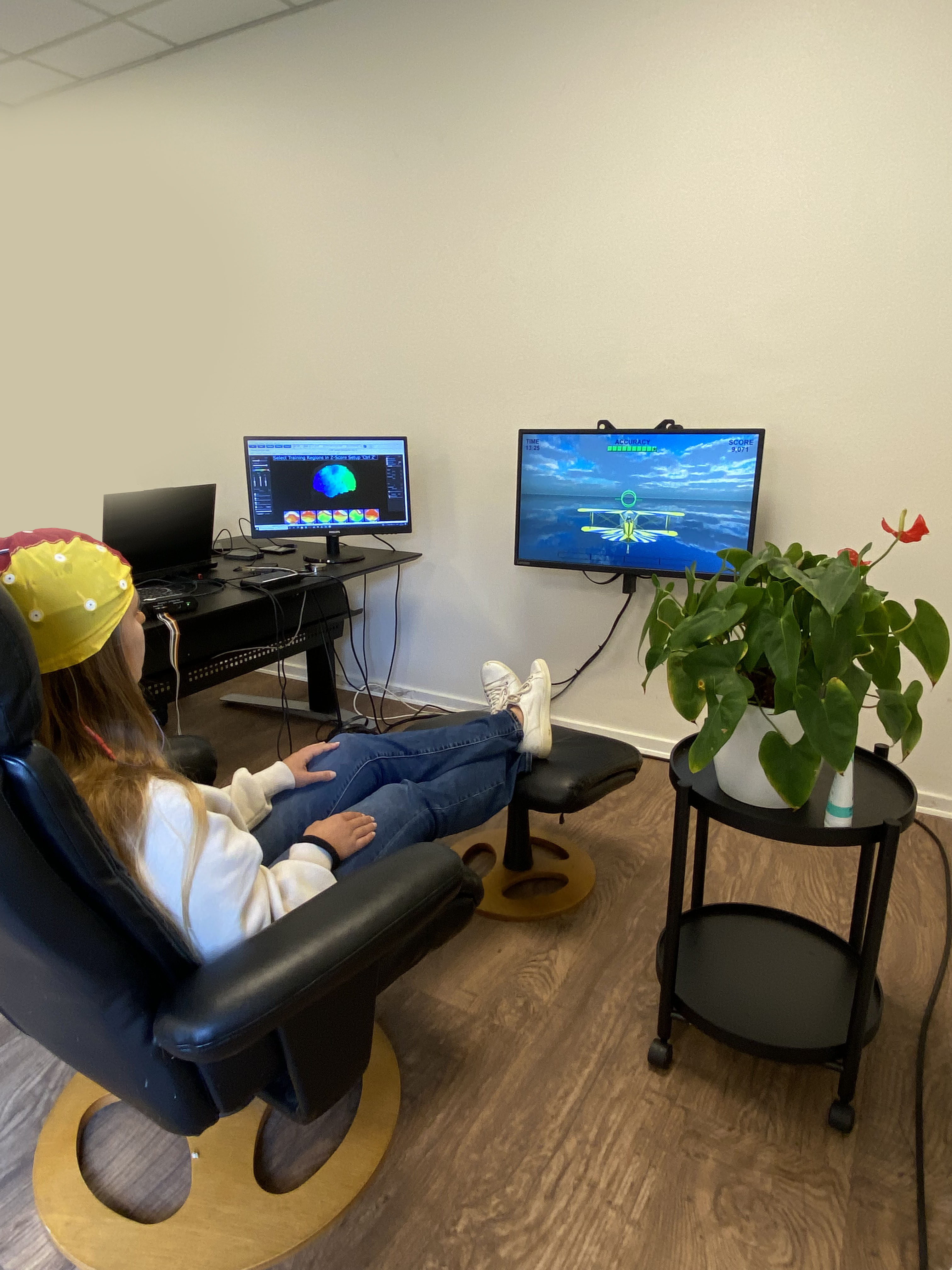

Træningsforløbet for børn med ADHD, autisme eller asperger
Barnet sidder foran en computerskærm, med en eller to aktive elektroder på hovedet, som måler hjernens elektriske aktivitet. Barnet bliver guidet gennem hele sessionen. For at træningen skal blive så motiverende som muligt, må barnet selv vælge animationerne eller filmen, der bliver vist på skærmen til træningen.
Når barnet er roligt og koncentreret, belønnes det med animationer i bevægelse på skærmen eller en DVD. Bliver barnet derimod uroligt, rastløs, falder i staver og mister koncentrationen, standser animationerne eller skærmen der viser filmen bliver sort.
Det er også muligt at medbringe egne dvd'er som kan bruges som feedback. Gennemsnitlig skal et barn have mellem 15 træningssessioner á 1 time.
Tilpasset forløb for ADHD, autisme eller asperger
Træningsforløbet tilpasses den enkelte klient, på baggrund af en QEEG-måling og samtale med forældrene om hvilke symptomer der er de vigtigste at fokusere på.
Gennem en analyse af QEEG-målingen ved hjælp af Loreta-databasen (som omdanner brainmappet til MRI-billeder), finder man forbindelsen mellem de symptomer, der ønskes at fokusere på og de relevante elektrodeplaceringer og frekvenser skal hæmmes eller øges.
Dermed kan man lave en træningsprotokol som er så præcis som mulig.
Ved at sammenligne QEEG-målingerne før og efter træning, får vi også en objektiv dokumentation på fremgang.
Tidligere metoder for ADHD, autisme eller asperger
Inden man indenfor neurofeedback-området benyttede brainmapping/QEEG-målinger benyttede man standard træningsprotokoller (beta-træning og SMR-træning). Hvor beta-træningen blev benyttet til at træne op arousalniveauet, mens SMR-træningen blev benyttet til at træne med den motoriske arousal. Se nedenfor.
Men QEEG-målinger viser at det er meget mere kompliceret, derfor vil disse to måder at træne på variere meget fra person til person og næsten aldrig vil en klassisk træningsprotokol benyttes, uden at der justeres på frekvenser og elektrodeplaceringer.
Hør mere om neurofeedback som ADHD behandling
Ønsker du at høre mere om hvordan neurofeedback kan hjælpe med ADHC, OCD eller autismespektrumforstyrrelser? Eller er du interesseret i at få en tid, så kan du kontakte Institut for Hjernetræning ved at ringe på telefon 27 29 11 12 eller sende en mail til kontakt@hjernetraening.dk.
Institut for Hjernetræning holder til i Taastrup nær Roskilde, Karlsunde og København.
Kontakt os og hør mere om hvad vi kan gøre for dig
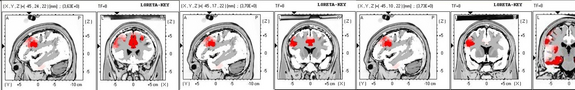
Eksempel på træningsforløb for dreng med OCD
De absolutte værdier inden træningsforløbet
De absolutte værdier efter træningsforløb
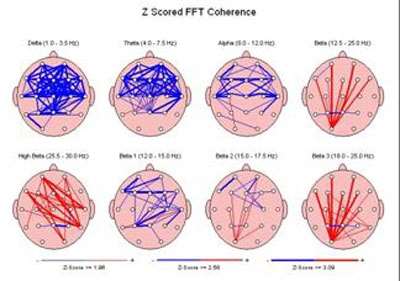
Coherencen inden træningsforløbet
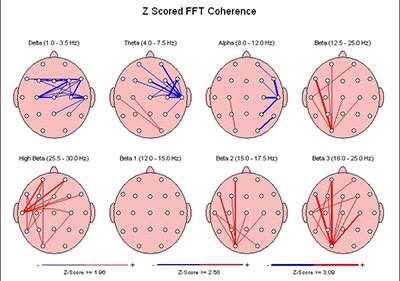
De absolutte værdier efter træningsforløb
Ovenfor ses brainmaps af en dreng med OCD før og efter et træningsforløb. De første brainmaps viser de absolutte værdier (mængden af hjerne-aktivitet) sammenlignet med en normativ EEG-database. Den grønne farve står for det normale, de blå farver for for lav hjerneaktivitet, mens den gule og røde farve står for for meget hjernaktivitet. Inden træningsforløbet ligger EEGet generelt for lavt, hvilket ses af den blå farve.
Efter træningsforløbet ligger EEGet inden for det normale, (den gule og røde aktivitet i panden på første billede kommer af øjenbevægelser og har ikke noget med hjernen at gøre)
De nederste brainmapa viser fordelingen af coherensen. Coherensen viser hvordan de forskellige områder i hjernen kommunikerer. De røde streger betyder for høj coherens og de blå streger betyder for lav coherense. Normalt skal der ikke være hverken røde eller blå streger. Brainmappet inden træningsforløbet er præget af for høj eller for lav coherens. I brainmappet efter træningsforløbet har coherensen normaliseret sig.
Forskning og AD/HD